Science : Term 1 Unit 5 : Reproduction and Modification in Plants
Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer.
1. Vegetative propagation by leaves takes place in
a. Bryophyllum
b. Fungi
c. Virus
d. Bacteria
Answer : a) Bryophyllum
2. Asexual reproduction in yeast is
a. Spore formation
b. Fragmentation
c. Pollinationd.
d. Budding
Answer : d) Budding
3. Reproductive part of a plant is
a. Rootb.
b. Stem
c. Leafd.
d. Flower
Answer : d) Flower
4. Pollinators are
a. Windb.
b. Water
c. Insectd.
d. All the above
Answer : d) All the above
5. Climbing roots are seen in
a. Betelb.
b. Black pepper
c. Both of themd.
d. None of them
Answer : c) Both of them
II. Fill in the Blanks.
1. The male reproductive part of a flower is androecium
2. Ovary is the basal swollen part of the Gynoecium.
3. After fertilization the ovule becomes seed
4. Breathing roots are seen in mangrove plants.
5. Onion and Garlic are example of bulb.
III. True (or) False, write the correct answer for the false statement.
1. A complete flower has four whorls. [True]
2. The transfer of pollen to the stigma is known as pollination. [True]
3. Conical shaped root is carrot. [True]
4. Ginger is an underground root. [False]
Ginger is an underground stem.
5. Leaves of Aloe vera are fleshy and store water. [True]
IV. Match the following:
1.Petal- Opuntia
2. Fern- Chrysanthemum
3. Phylloclade- Attracts insect
4. Hooks- Spore
5. Sucker- Bignonia
Answer :
1. Petal – Attracts insect
2. Fern – Spore
3. Phylloclade – Opuntia
4. Hooks – Bignonia
5. Sucker – Chrysanthemum
V. Very short answer.
1. Write two types of reproduction in plants.
The two types of reproduction in plants are sexual and asexual reproduction.
2. What are the two important parts of a flower?
The two important parts of a flower are androecium and gynoecium.
3. Define – pollination.
The process by which pollen grains reach stigma is called as pollination.
(Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called pollination)
4. What are the agents of pollination?
The agents of pollination are wind, water, insects, birds and animals.
5. Give example for
a. Corm b. Tuber
a. Corm – Colocasia
b. Tuber – Potato
6. What is tendril?
In climbers, the leaf of plant are modified into elongated structure to help the plants to climb efficiently. They are called tendrils.
7. What are thorns?
In Opuntia the leaves are reduced to small spines with less surface area. It is an adaptation to reduce transpiration.
VI. Short answer.
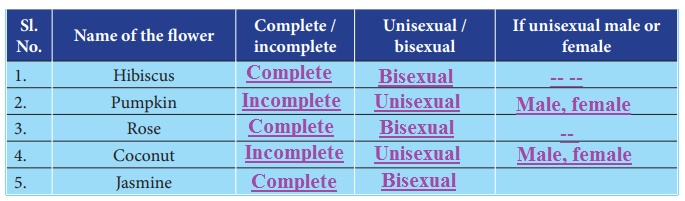
1. Differentiate bisexual flower from unisexual flower?
Flowers having both androecium and gynoecium are called bisexual flowers.
Flowers having either androecium or gynocium are called unisexual flowers.
2. What is cross pollination?
Pollen grains are transfered from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same kind or different plant. This is called cross pollination.
3. Write notes on phyllode.
In Acacia auriculiformis petioles expand to form leaf like structure. They carry out the function of leaf (photosynthesis).
VII. Answer in Details.
1. Write a brief account on pollination.
Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower is called pollination.
Transfer of pollen grains from male flower to the female flower by us is called artificial pollination. However in nature there are many ways in which pollen grain reach the stigma of a flower and it is called natural pollination.
There are two types of pollination :
1) Self – pollination
2) Cross – pollination

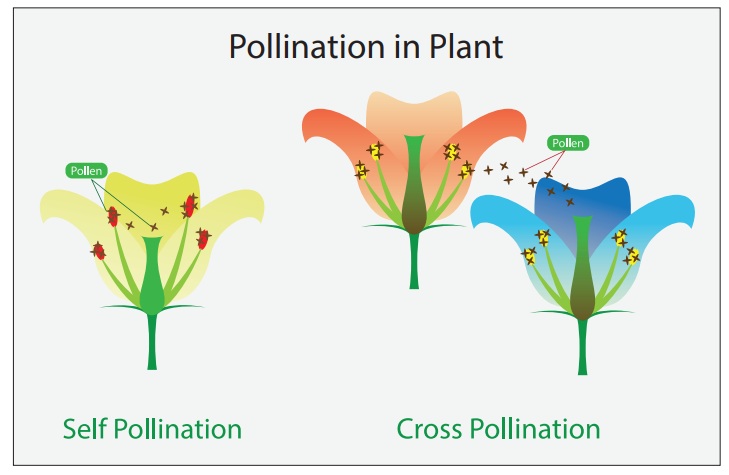
Pollen grains are transferred from one anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant. This is called self pollination. This process doesn’t need any pollinators. Plants do not need to produce pollen grains in a large quantity for self pollination.
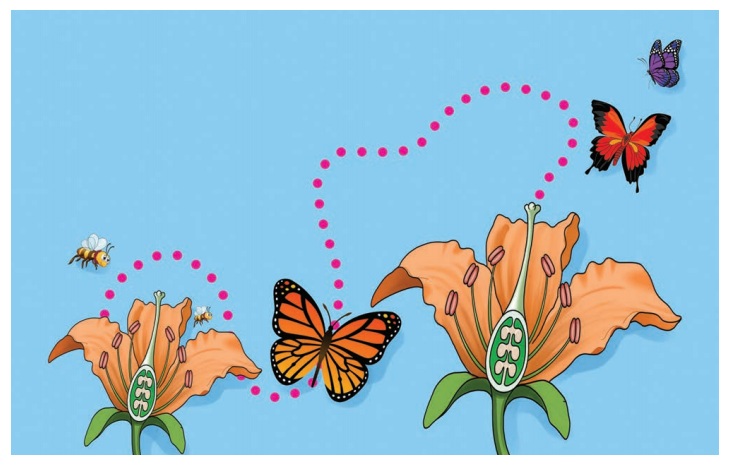
Pollen grains are transfered from another of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same kind or different plant. This called cross pollination. Plants need to produce pollen grains in larger quantities to increase the chance of pollination. It requires various pollinators like wind, water, insect and animals.
2. Explain the underground stems.
In most of the plants stem grows above the ground but there are some stems that grow under the ground. They store food for the plant stem. There are four types of underground stems :
i) Rhizome ii) Corm iii) Tuber iv) Bulb
i) Rhizome :
It is an underground thick stem with node and intemodes with scale leaves at the node. It grows horizontally and has an irregular shape. Rhizome have buds.
They give rise to new stem and leaf.
Eg. Ginger and Turmeric

ii) Corm :
This underground stem is round in shape and flat at the top and bottom. It is a condensed form of rhizome and bears one or more buds in the axils of scale leaves. Daughter plants arise from their buds. Eg. Colocasia

iii) Tuber:
It is an enlarged, spherical underground stem that store food. It has many dormant buds on its surface known as “Eye”. If we plant a part of tuber with the bud, it grows in to a new plant.
E.g. Potato

iv) Bulb :
It is a condensed stem which is disc like and stores food in the fleshy leaves. The bulb has two types. (1) Fleshy leaves (2) Scaly leaves. The upper part of the stem has a terminal bud and it is covered by many scale leaves. The inner fleshy leaves store food as seen in Garlic and Onion.

VIII. Higher Order Questions.
1. Ginger is considered to be a stem, not a root. Why?
Ginger is considered to be stem because it has nodes and intemodes. Node is covered with scale leaves and buds.
2. What will happen if pollen grain of rose gets deposited on stigma of lily flower? Will pollen germination takes place? Why?
No, because both flowers are different species. There will be no germination of pollen grains.
IX. Assertion and Reasoning types of Question.
1. Assertion – Pollination and fertilization in flowers, produces fruits and seeds.
Reasoning – After fertilization the ovary becomes fruit and ovule becomes seed.
a. Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect.
b. Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is correct.
c. Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct.
d. Assertionis incorrect, Reasoning is incorrect.
Answer: 1) c. Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct.
2. Assertion – The example of conical root is carrot.
Reasoning – It is an adventitious root modification.
a. Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is correct.
b. Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is incorrect.
c. Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct.
d. Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect.
Answer: 2) d. Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect.
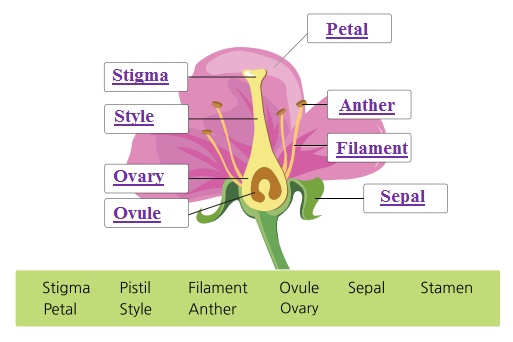
X. Picture Based question.
i. Observe the picture and draw the labels.
Parts of a Flower
Stigma Pistil Filament Ovule Sepal
Petal Stamen Style Anther Ovary
ii. Identify the four plants shown in the following Name the different modification in each of them.
Name – Modification
1. Banyan – Mechanical support
2. Nepenthus – Trap
3. Eichhomia – Sub-aerial modified root
4. Stolon – Wild Strawberry
Student Activities
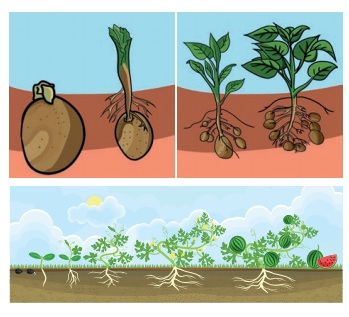
ACTIVITY 1
Aim:
To raise a new generation of plant from watermelon and potato.
Materials required:
Two pots with soil, potato, watermelon seeds and water.
Procedure:
Fill both pots with soil mixed with compost or manure. Take young potato. Ensure that it is not dried up and the skin still looks fresh. Bury a potato in one part. Sow watermelon seeds in another pot. Pour water regularly and maintain the plant
Observation:
After few days, we can see single plant arising from a buried potato. Plants arise from the pot sowed with watermelon seeds. Each seed produces a plant
Inference:
Watermelon plants were produced from seeds. Potato plant is not from seed, but from the stem tuber (vegetative part). Seed is not only the source for new generation, even vegetative part of a plant can also be used to produce a new plant.
ACTIVITY 2
Take a flower. Dissect as shown longitudinally and find parts inside the flower. Can you identify the male reproductive part, androecium (stamen, filament and pollen sac). Carefully observe the female reproductive part, gynoecium (ovary, style and stigma). If they are not seen clearly, gently pluck off the sepals and petals. Make a drawing of the parts and arrangement in your notebook.
ACTIVITY 3
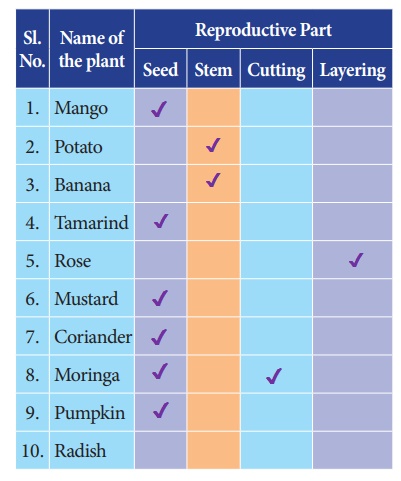
Using the information from the above complete the following table:
The sunflower is not asingle flower. It is a group of flowers clustered together. A group of flowers arranged together is called inflorescence. Tridax procumbens, looks like a single flower, but is an inflorescence. Leaf juice of this plant is used to cure wounds and cuts.
ACTIVITY 4
Make a flower album
Press the collected flowers between pages of newspaper or book. Place two thick sheets and keep a heavy object, such as brick, on the top to apply pressure. Turn the sides every two to three days. Allow flowers to dry completely. Collect the dried flowers and paste them in an album. Now, your flower album ready.
1. The world’s largest and heaviest seed is the double coconut. The seed looks liketwo coconut fused together. It only grows in two islands of the Seychelles. A single seed may be 12 inches long, nearly 3 feet in circumference and weighs about 18 kg.
2. Orchids have the smallest seeds in the plant kingdom. 35 million seeds may weight only about 25 gram.
ACTIVITY 5
Aim: To study the modification of root.
Materials Required: Sample / charts of raddish, carrot, beet root, sweet potato, stilt roots and pneumatophores.
Procedure: Carefully observe the shape of each specimen.
Observation: Draw the diagram and observe the morphological differences between the samples.
ACTIVITY 6
Aim: To study the modification of stem Materials Required: Specimens of Ginger, Potato, Onion, Mint, Bougainvillea–, Acacia, Opuntia and locally available specimens.
Procedure: Observe the external morphology of each specimen.
Observation: Draw diagram and bring out the differences and their function in each type of stem modifications.
