English : Unit 6 : Prose : Friendship
Warm up
1. Do you have any childhood friendship that is still strong today?
Answer: Yes, I have two childhood friends Deepthi and Brindha, who are still strong today.
2. Do you make friendship with others easily?
Answer: Yes, I do make friendship with others easily.
3. Share an incident that you remember proudly about your friends.
Answer: Last year, when I was in seventh standard, we had an elocution competition in English and a skit to be played during the annual school day. We planned to do a play on ‘Merchant of Venice’ with my mother’s help. My mother is a teacher in another school.
I was good at spoken English. So I helped my friends to speak the dialogues well. My mother also guided them in performing their character’s absolutely well. We performed on the stage and won the first prize. I also helped some of them in the Elocution competition. Two of them bagged the first and second prizes. I was really proud of all my friends, as they were able to grasp very quickly, what was told to them. They were so humble to tell everyone that it was I who helped them to win the prizes. I was so happy and proud to have such good friends.
Glossary
Section –I
complexes – consisting of many different and connected parts
demanded – ask authoritatively
establish – set up on a firm and permanent basis
decided – having clear opinion
Section –II
boarded – get on or into a vehicle
consoled – comfort someone at the time of grief
exchanged – give something and receive something
competition – an event or contest
affected – cause a change in someone or something
Section –III
nervously – in an anxious or uneasy manner
astounded – shocked or greatly surprised
hesitatingly – to be reluctant or wait to act because of fear
dumbfounded – speechless with amazement
dropped – the act of a person or thing that drops
Questions Answers
Section –I
Fill in the blanks
1. Vetri constructions was once a leading company.
2. He took a loan to run his company.
3. Vetri’s friend is Asif
Section –II
Say True or False.
1. Keelakudi was the native of Vetri. [Answer: True]
2. The school was a middle school. [Answer: True]
3. Vetri and Asif were good in studies. [Answer: True]
4. Vetri never visited Chennai. [Answer: True]
5. Asif was a businessman. [Answer: True]
Section –III
Read and Understand
A. Choose the correct answer.
1. Vetri went to Asif’s ____________.
a) home
b) office
c) room
[Answer: (b) office]
2. Vetri came to Chennai to visit his ____________.
a) father
b) friend
c) brother
[Answer: (b) friend]
3. Asif saw his friend through the ____________.
a) camera
b) window
c) glass
[Answer: (a) camera]
B. Choose correct synonyms for the italic word.
1. Vetri constructed a bungalow.
a) designed
b) built
c) demolished
d) destroyed
[Answer: (b) built]
2. The brothers started a business separately.
a) apart
b) alone
c) united
d) combined
[Answer: (a) apart]
3. I am living in the outskirts of the village.
a) border
b) outpost
c) center
d) region
[Answer: (b) outpost]
4. Asif quarreled with his friend.
a) fought
b) differ
c) peace
d) fun
[Answer: (a) fought]
5. He stood astounded.
a) happy
b) surprised
c) shocked
d) excited
[Answer: (c) shocked]
C. Choose correct antonyms for the italic word.
1. Verti’s wife replied angrily.
a) calmly
b) annoyed
c) irritate
[Answer: (a) calmly]
2. The vegetables look fresh.
a) rotten
b) dull
c) new
[Answer: (a) rotten]
3. Vetri had a strong will to start a new business.
a) desire
b) thin
c) weak
[Answer: (c) weak]
4. Vetri was surprised by his friend.
a) unsurprised
b) expected
c) shocked
[Answer: unsurprised]
5. He spoke nervously.
a) Scared
b) confident
c) anxious
[Answer: (b) confident]
D. Answer the following questions in one or two words.
1. What was the name of Vetri’s company?
Answer: The name of Vetri’s company was ‘Vetri Constructions’.
2. Why did he sell his properties?
Answer: He sold his properties to pay his loans.
3. Which was the home town of Vetri and Asif?
Answer: The home town of Vetri and Asif was Keelakudi village.
4. When was the school established?
Answer: The school was in the outskirts of Keelakudi village. It was a middle school.
5. When did Vetri receive a call from Asif’s office?
Answer: Two days later after reaching his home, Vetri received a call from Asif’s office.
E. Answer the following questions in 100 words.
1. How did Vetri lose his properties?
Answer: Vetri was once a successful businessman in Coimbatore. His Vetri constructions was a leading construction company. After his father’s death, his brothers demanded to split the wealth, as they wanted to start their business separately. From then on, Vetri found it difficult to establish his business. He took loans to run his company, but he could not pay the loan. So he sold all his properties and paid the loans. His family then moved to a very small house. He found a job and started to lead a normal life.
2. What happened when Vetri met Asif?
Answer: Vetri boarded the train and went straight to Asif’s office. When Vetri was enquiring about Asif, he got a pat on his back. It was Asif, who came to receive Vetri, after seeing him through the CCTV camera. Vetri was speechless. He apologized to Asif saying that he never got a chance to visit Chennai. So he couldn’t meet him at all. They spoke about their school days and the fun they had. They also discussed about their business. Asif took Vetri to his home for lunch. Vetri was surprised to see that everyone knows him. In the evening, Asif dropped him at the station.
3. How did Asif show his friendship?
Answer: Asif was a true friend of Vetri. When Vetri came to his office, he came to receive him, as he saw through the CCTV camera. He gave Vetri a pat on his back. Vetri was speechless on seeing him. He took to his cabin. They spoke about their school days and the fun they had. They discussed about their business. Asif took Vetri to his home for lunch. Vetri was surprised to see that everyone knows him. Vetri stayed there till evening. Asif dropped him in the railway station. After two days, he invited Vetri to his office and assigned him a project.
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
Short Questions with Answers.
1. What did Vetri’s Constructions construct?
Answer: Vetris constructions constructed many shopping complexes, houses and a few apartments in and around Coimbatore.
2. What happened after his father’s death?
Answer: After his father’s death, his brothers demanded to split the wealth, as they wanted to start their business separately.
3. Whom did Vetri decide to meet? Why?
Answer: Vetri decided to meet his friend Asif in Chennai for help.
4. How strong was their friendship?
Answer: Vetri and Asif studied in the same school at Keelakudi village. They were always together in learning and playing. They continued to be good friends till their X Std. After that, Asif had to move to Chennai.
5. Who stopped Vetri at the gate of Asif’s office?
Answer: The security stopped Vetri at the gate and asked whom does he wants to meet.
6. How did Asif know that Vetri had come to his office?
Answer: Asif saw him through the CCTV camera and came to receive him.
7. Why didn’t Vetri’s wife ask anything else?
Answer: Vetri fold his wife everything in detail. His wife knew her husband. So she didn’t ask anything else.
Paragraph Question with Answer.
1. How did Vetri and Asif’s friendship start?
Answer: Their friendship started on the first day of school. When Vetri’s parents dropped him at the school, he started crying. Asif consoled him with a chocolate and asked him not to cry. From that day, they stayed together, played together and even exchanged their food. Their friendship grew stronger with time. They were always good in studies and helped each other in lessons. There was always a healthy competition between them. Surprisingly, the exams, results and marks never affected their friendship. Their friendship continued till tenth standard. Then Asif moved to Chennai.
Vocabulary
Commonly Confused Words.
The error with this pair results from mispronunciation and failure to distinguish between a noun and a verb.
Example:
Advice/Advise
The c in advice is pronounced with the sound of /s/. Advice is a noun meaning “recommendation regarding a decision”.
The s in advise is pronounced with he sound of /z/. Advise is a verb meaning ‘to recommend’.
1. Complement : It is something that completes something else.
Compliment : It is a nice thing to say.
2. Empathy : It is the ability to understand another person’s perspective or feelings.
Sympathy : It is a feeling of sorrow for someone else’s suffering.
3. Inquiry : Inquiry and enquiry both mean ‘a request for information’. It is the standard American English spelling.
Enquiry : It is the British spelling.
4. Stationary : It means unmoving.
Stationery : It refers to letter writing materials and especially to high quality paper.
5. Effect : An effect is a result or a consequence. (usually a noun) Effect may also
function as a verb meaning “to bring about something.”
Affect : An affect is to have an impression, influence, or effect on something.
(usually a verb) .
6. Lie : Use lie when the object is laying itself down.
Lay : Use lay when the object is being laid down.
7. Rise : Use rise when the object is lifting itself.
Raise : Use raise when the object is being risen by another force.
Complete the following sentences using appropriate confusable words.
1.The sugar had a negative effect on the science experiment. (effect/affect)
2. I am going to lie down for an hour. (lie/lay)
3. The gas prices continue to rise (raise/rise)
4. She always gives me good advice. (advice/advise)
5. The war had no effect on oil prices. (affect / effect)
VOCABULARY –ADDITIONAL
CONFUSED WORDS
1. Can you __________ ( here / hear) me?
[Answer: hear]
2. Last_________(weak I week) I did not attend the school.
[Answer: week]
3. It is a very beautiful_______________ (seen I scene).
[Answer: scene]
4. He tried to__________ (steel / steal) the gold chain.
[Answer: steal]
5. The hunting dogs tried to_______(haul I hall) the wolf.
[Answer: haul]
Anagram
An anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of another word or phrase. Anagrams can be useful by helping a learner become aware of both spelling and spelling patterns.
Example:

Exercise:

Antigram
Anagrams are words or phrases created by rearranging the letters of another word or phrase. An anagram becomes an antigram when it is opposite in meaning to the original word or phrase.
Example:

Exercise:

ANAGRAM
1. Elbow [Answer: Below]
2. State [Answer: Taste]
3. Cat [Answer: Act]
4. Arc [Answer: Car]
5. Sale [Answer: steal]
6. School master [Answer: The classroom]
ANTIGRAM
1. Indeed [Answer: Denied]
2. Inferno [Answer: Non-fire]
3. Tip [Answer: pit]
4. Silent [Answer: Listen]
5. forty five [Answer: Over fifty]
Listening
Listen carefully to the passage and answer the following questions
Dear friends!
This is Rahim. I hope you will lend your ears for two minutes to me on this happy occasion of the 13th birthday of my friend Rahul. Before he blows out candles on his cake and cut the cake to mark the first day in his 13th year, I would like to share few words with you. Rahul and I grew up from kids. He is an open book for me and for everyone. I have observed the fine determination he is built with. His strong friendship has stood by me many times. When I hurt him, he wrote over the sand. When I help him, he engrave it in his heart. Only if you’re lucky, you’ll find a person like him who brightens your day, lends an ear, and inspires you. I am grateful to him for life.
He excelled in various ways already in his life. I wondered his ability to do well in whatever he found himself engaged in. Besides being a good student, he has done well in sports and games. He is always in the front line and bagged ‘all-rounder’ medal in school.
I wish him all the happiness with which he should sail through life. Best of luck to you Rahul, and May we always see you smiling like this. Please give him a big hand!
Questions:
1. Whose speech is this?
Answer: It is Rahim’s speech.
2. What did Rahul engrave?
Answer: Rahul engraved Rahims help in his heart.
3. Who is lucky?
Answer: Rahim is lucky.
4. Who bagged ‘all-rounder’ award?
Answer: Rahul bagged all-rounder medal in school.
5. Whose birthday party is it?
Answer: It was Rahul’s birthday party.
Speaking
Picture description
Describe the things in the picture using the descriptive words given below.

Writing
Forms
Some application forms are very simple. They are used for opening a bank account, booking tickets, applying to institutions, etc. You need to give information about your yourself, address, e-mail id, phone number, date of birth and other details etc.
Steps to fill in forms
i. Take a photocopy of the application.
ii. Use a pencil to fill in the application in the photocopy.
iii. All the entries in the application should be filled in English/Regional language as required.
iv. Fill in forms in capital letters.
v. Give your full address with pincode.
vi. Write legibly.
vii. Don’t over write or score out.
viii. Give only required details.
ix. Don’t forget to sign/ get attestations.
x. Mention the date of applying.
xi. Double check before filling the original form in ink.
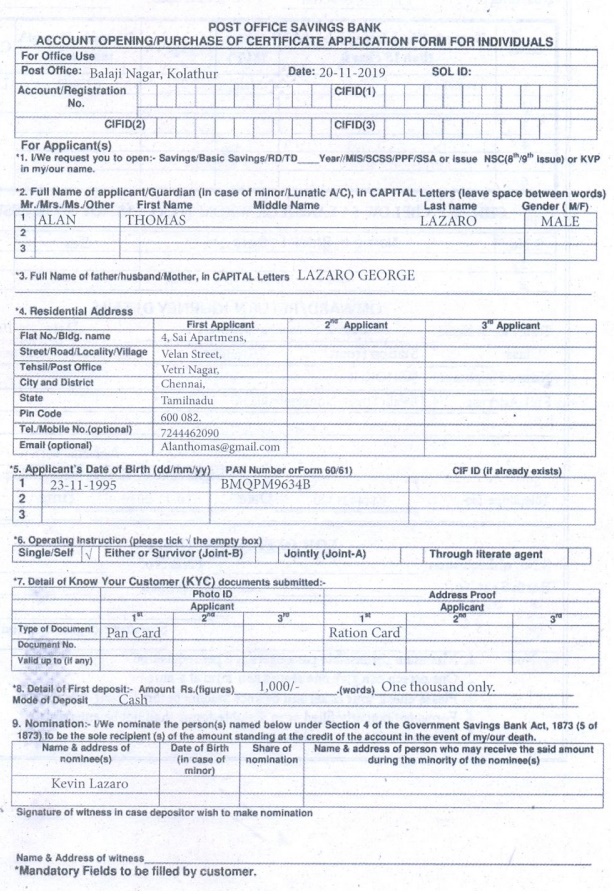
Given below is a filled in bank challan to obtain a Demand Draft

H. Fill in the Form given below.
Answer:
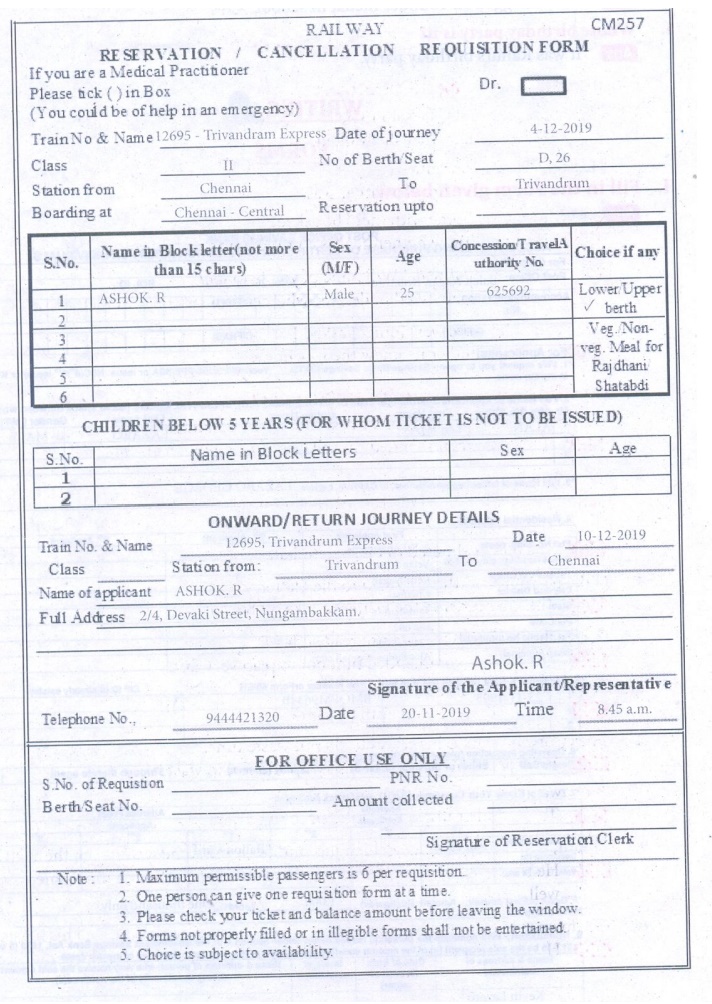
I) Fill in the Form given below.
Grammar
PICTO GRAMMAR
REPORTED SPEECH

In the above picture Smith said something to Arun then Arun reports what Smith said to him in the other pictures, this is known as reported speech. First Arun used the exact words of Smith, it is direct speech then he said in his own words it is indirect speech. Thus, we can report a conversation in two types.
The things that we have to concentrate when we report a speech.
* Reporting verbs (Smith said that he would come the next day.)
* Conjunctions (Smith said that he would come the next day.)
* Pronoun (Smith said that he would come the next day.)
* Tenses (Smith said that he would come the next day.)
* Adverbs (Smith said that he would come the next day.)

Direct – Kaitlyn said. “I am very busy now.”
Indirect – Kaitlyn said that she was very busy then.
* Two verbs commonly used while reporting are told and said.
He said (that) he was cooking dinner.
He told me (that) he was cooking dinner.
Did you notice that tell/told has been used in the sentence which mentions the listener?
In reported speech we need not mention the listener when we use say/ said.
He said (that) he was cooking. [listener not mentioned)
In direct speech we say: Rahim said to me, ‘I will be waiting here.’
In Direct Speech, we use inverted commas to mark off the exact words of
the speaker. In Indirect Speech we do not.
Rules for changing Direct Speech into Indirect.
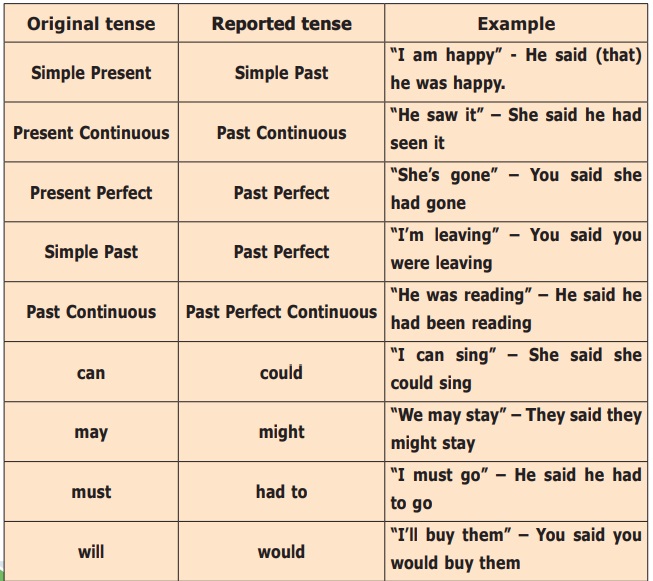
When the reporting or principal verb is in the Past Tense, all Present tenses of the Direct are changed into the corresponding Past Tenses. Thus:-
(a) A simple present becomes a simple past.
Direct – He said, “I am fine.”
Indirect – He said (that) he was fine.
(b) A present continuous becomes a past continuous.
Direct – She said, “My sister is learning Bharatanatyam.”
Indirect – She said (that) her sister was learning Bharatanatyam.
(c) A present perfect becomes a past perfect.
Direct – He said, “I have won the match.”
Indirect – He said (that) he had won the match.
(d) The shall and the will of the Future Tense is changed into should and would.
(e) The simple past in the Direct becomes the past perfect in the Indirect.
Direct – She said, “The horse died in the night.”
Indirect – She said that the horse had died in the night.
(f) The tenses may not change if the statement is universal truth.
Direct – The teacher said, “The earth goes round the sun.”
Indirect – The teacher said the earth goes round the sun.
(f) If the reporting verb is in the Present Tense, the tenses of the Direct Speech do not change.
For example, we may rewrite the above examples, putting the reporting verb in the Present Tense, thus:
He says he is fine.
She has just said her sister is learning Bharatanatyam.
He says he has won the match.
She says the horse died in the night.
(g) Words expressing nearness in time or place are generally changed into words expressing distance. Thus:-
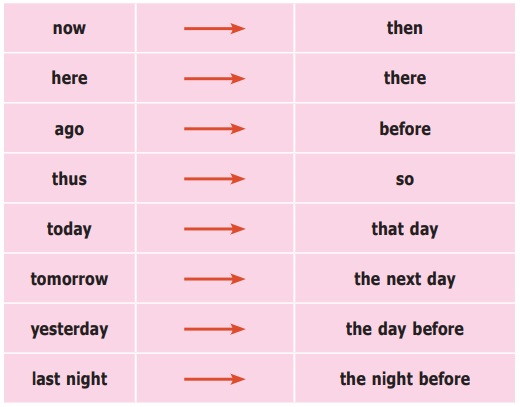
Direct – The Prince said, “It gives me great pleasure to be here this evening.”
Indirect – The Prince said that it gave him great pleasure to be there that evening.
(h) The changes do not occur if the speech is reported during the same period or at the same place.
Direct – The Prince said, “It gives me great pleasure to be here this evening.”
Indirect – The Prince said that it gives him great pleasure to be here this evening.
Questions
In reporting questions the Indirect Speech is introduced by some verbs as asked, enquired, whether or if etc.
Direct – He said to me, “What are you doing?”
Indirect – He asked me what I was doing.
Direct – “Where do you live?” asked the stranger.
Indirect – The stranger enquired where I lived.
Direct – He said, “Will you attend the meeting?”
Indirect – He asked them whether they would attend the meeting.
A) Change the following into Indirect Speech:-
1. “What do you want?” he said to her.
Answer: He asked her what she wanted.
2. He said, “How’s your father?”
Answer: He enquired how his father was.
3. “Are you coming home with me?” he asked.
Answer: He asked him whether he was coming home with him.
4. The poor man exclaimed, “Will none of you help me?”
Answer: The poor man asked in despair whether none of them would help him.
5. “Don’t you know the way home?” asked I.
Answer: I asked whether he knew the way home.
Commands and Requests
In reporting commands and requests, the Indirect Speech is introduced by some verbs as ordered, requested, commanded, shouted, urged etc.
Direct – Rama said to Arjun, “Go away.”
Indirect – Rama ordered Arjun to go away.
Direct – He said to him, “Please wait here till I return.”
Indirect – He requested him to wait there till he returned.
Direct – “Call the first witness,” said the judge.
Indirect – The judge commanded them to call the first witness.
Direct – He shouted, “Let me go.”
Indirect – He shouted to them to let him go.
Direct – He said, “Be quiet and listen to my words.”
Indirect – He urged them to be quiet and listen to his words.
B) Change the following into Indirect Speech
1.“Bring me a glass of milk,” said the swami to the villagers.
Answer: The swami commanded the villages to bring him a glass of milk.
2. “Sit down, boys,” said the teacher.
Answer: The teacher ordered the boys to sit down.
3. “Halt!” shouted the officer to his men.
Answer: The officer shouted to his men to halt.
4. “Take off your hat,” the king said to the Hatter.
Answer: The king ordered the Hatter to take off his hat.
5. The teacher said to him, “Do not read so fast.”
Answer: The teacher commanded him not to read very fast.
6. He said to me, “Wait until I come.”
Answer: He urged me to wait until he came.
7. “Hurry up,” he said to his servant, “do not waste time.”
Answer: He ordered his servant to hurry up and not to waste time.
8. “Run away, children,” said their mother.
Answer: Their mother urged the children to run away.
9. He said, “Daughter, take my golden jug, and fetch me some water from the Well.”
Answer: He requested his daughter to take his golden jug and fetch him some water from the well.
10. “Go down to the bazaar. Bring me some oil and a lump of ice.” ordered his master.
Answer: His master ordered him to go down to the bazaar and bring him some oil and a lump of ice.
D) What were the actual words used in each instance below? The sentences containing the actual words are jumpled in the box. Write them out in the same order as the actual words.
1. Punitha asked Pushpa what she was reading.
2. Pushpa told her that he was reading Robinson Crusoe.
3. Punitha asked her what it was all about.
4. Pushpa said it was about a man wrecked on an island.
5. Punitha then asked her friend who gave her the book.
6. Pushpa answered that her uncle gave it to her at Christmas.
7. Finally Punitha inquired if she could borrow it.
8. Pushpa replied that she would certainly lend it to her.
(a) “May I borrow it?” inquired Punitha.
(b) “What are you reading, Pushpa?” asked Punitha.
(c) “It is about a man wrecked on an island,” Pushpa said.
(d) “Of course I will lend it to you,” replied Pushpa.
(e) “Uncle gave it to me at Christmas,’ answered Pushpa.
(f)”What is it all about?” Punitha asked.
(g)”I am reading Robinson Crusoe, Pushpa told her.
(h)”Who gave you the book, Pushpa?” Punitha then asked.
Answer:
1. (b) “What are you reading, Pushpa?” asked Punitha.
2. (g) “I am reading Robinson Crusoe”, Pushpa told her.
3. (f) “What is it all about?” Punitha asked.
4. (c) “It is about a man wrecked on an island,” Pushpa said.
5. (h) “Who gave you the book, Pushpa?” Punitha then asked.
6. (e) “Uncle gave it to me at Christmas,’ answered Pushpa.
7. (a) “May I borrow it?” inquired Punitha.
8. (d) “Of course I will lend it to you,” replied Pushpa.
E. Change the following into Direct Speech:-
1. Nevin asked his father when the next letter would come.
Answer: Nevin asked his father, “When will the next letter come?”
2. I wrote that I would visit him next day.
Answer: I wrote, “I will visit you tomorrow”.
3. I told them to be quiet.
Answer: I said to them, “Be quiet”.
4. Lakshan asked me if I had anything to say.
Answer: He asked me, “Do you have anything to say”.
5. An old mouse asked who would bell the cat.
Answer: An old mouse asked, “Who will bell the cat?”
6. Mervin said that he wanted to be a soldier.
Answer: Mervin said, “I want to be a soldier”.
7. Ebin asked me what I wanted.
Answer: Ebin asked me, “What do you want?”
8. Bhagya said that she had seen that picture.
Answer: Bhagya said, “I have seen this picture”.
9. The stranger asked Nasrin where she lived.
Answer: The stranger asked Nasrin, “Where do you live?”
10. I asked Mary if she would lend me a pencil.
Answer: I asked Mary, “Will you lend me a pencil?”:
F. Sherlyn receives a postcard from her friend Pushpa who is holidaying in Sri Lanka. She calls her friend Galen and tells him what Pushpa has written. Help her by filling in the blanks, using reported speech.

Hello, Galen Today I received a postcard from Pushpa. Remember I had told you that She has gone to Sri Lanka on a holiday? Well, she has written from Colombo. She has written that she had visited Pinnawala Elephant Orphanage. It had 84 elephants. She said that it is the biggest herd of elephants in the world that is living under human supervision. She also added that she she was glad that they had come there because she was learning a lot . The Elephant Orphanage was truly worth visiting. She said that next day, they are going to the national park. She would be returning next week and added that she was looking forward to meeting me then.
GRAMMAR ADDITIONAL
REPORTED SPEECH
A. Change the following into indirect speech :
1. Ramu says, “I am busy”.
Answer: Ramu says that he is busy.
2. Suresh said, “I like dancing”.
Answer: Suresh said that he liked dancing.
3. He said, “I am going to the cinema”.
Answer: He said that he was going to the cinema.
4. Ravi said, “I have bought a cycle”.
Answer: Ravi said that he had bought a cycle.
5. Ram said, “Visu came at night”.
Answer: Ram said that Visu had come at night.
6. He said, “Honesty is the best policy”.
Answer: He said that honesty is the best policy.
7. She said, “I have done my homework”.
Answer: She said that she had done her homework.
8. He says, “I am happy”.
Answer: He says that he is happy.
9. The teacher said, “Hari will definitely pass”.
Answer: The teacher said that Hari would definitely pass.
10. Raju said, “I shall be here this evening”.
Answer: Raju said that he would be there that evening.
B. Change the following into direct speech :
1. The teacher ordered the boys to leave that place.
Answer: The teacher said to the boys, “Leave this place”.
2. I requested him to give me a glass of water.
Answer: I said to him, “Please give me a glass of water”.
3. The captain ordered the soldiers to stand at ease.
Answer: The captain said, “Stand at ease”.
4. My brother said that he might go to Kolkata.
Answer: My brother said, “I may go to Kolkata”.
5. He said that the earth moves around the sun.
Answer: He said, “The earth moves around the sun”.
6. Ravi asked Ganesh when he was going to the library.
Answer: Ravi said to Ganesh, “When are you going to the library?”.
7. The policeman ordered the boy to show him his licence.
Answer: The policeman said to the boy, “Show me your licence”.
8. She told him that she was going to the market then.
Answer: She said to him, “I am going to the market now”
9. He said that he was buying a cell phone that day.
Answer: He said, “I am buying a cell phone today”.
10. He asked who I was.
Answer: He said, “Who are you?”.
C. Change the following into Indirect Speech :
1. He said, “My God! I am ruined.”
Answer: He exclaimed sadly that he was ruined.
2. He said, “Alas! our foes are too strong.”
Answer: He exclaimed sorrowfully that their foes were too strong.
3. “How smart you are!” she said.
Answer: She exclaimed that he was very smart.
4. He said. “Oh ! that’s a nuisance.”
Answer: He exclaimed with disgust that it was a nuisance.
5. He said, “What a pity you did not come!”
Answer: He exclaimed with sorrow that he did not come.
D. Convert the following into indirect speech.
a. Sharun said to me, Are you coming to school tomorrow?’
Answer: Sharun asked me if I am coming to school, the next day.
b. “We must visit the historical buildings of Delhi since we are here,’ said Ashok.
Answer: Ashok said that they had to visit the historical building of Delhi, since they were there.
c. ‘Have you read The Wind in the Willows?’ asked Amutha.
Answer: Amutha asked whether he had read ‘The Wind in the Willows’.
d. Teacher said to us, ‘You must conduct the experiment very carefully.’
Answer: The teacher told us that we had to conduct the experiment very carefully.
e. ‘Wow! That is great news!’ said Tejeswar.
Answer: Tejaswar exclaimed happily that it was a great news.
Language Check Point
1. Incorrect: Jim and me are going to the beach.
Correct: Jim and I are going to the beach.
Explanation: Don’t use objective pronoun ‘me’. Use ‘I’ as it plays a role of subject. (Jim and I – plural subject so we use are)
2. Incorrect: You better to consult a doctor.
Correct: You better consult a doctor.
Explanation: Don’t use infinitive to after rather and better.
3. Incorrect: They selected him as a leader.
Correct: They selected him a leader.
Explanation: ‘As’ is not used with the verbs like selected, elected, made, appointed , named and called.














