Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : Matter and Materials
UNIT 2
Matter and Materials

Learning Objectives
After completing this lesson students will be able to:
• know about matter and materials.
• understand the process of manufacturing fabrics.
• know the varieties of grains and the food products.
• understand why do things float or sink.
Introduction
Our needs have increased in the modern days and we use number of things in our daily life. We get some of them from the nature and some other things are manufactured artificially. The things you use like pen, pencil, ink, eraser, note book, ball and the food you eat, all have different nature and characteristics. They are obtained by transforming the natural and artificial substances. In this lesson we will study about different things used in our life and how they are obtained.
I. States of Matter
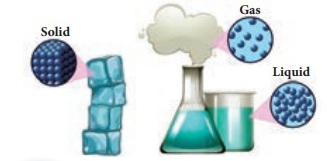
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Matter can exist in three physical states: solid, liquid and gas. It is made up of molecules and the molecules are made up of atoms.
• Solid
In solids molecules are very closely arranged. Solids are incompressible. They have definite shape, size and volume.
• Liquids
In liquids molecules are loosely packed. Hence, liquids are negligibly compressible. They have definite volume, but no definite shape and size.
• Gas
In gases, molecules are very loosely packed. Hence, gases are highly compressible.
Activity 1
Look at your surrounding. Give some examples for solids, liquids and gases. Solids Liquids gases
II. Materials
A material is a mixture of substances that constitute an object. They can be pure or impure, natural or man made. Materials are needed to get the things needed for our daily life. We need food, dress and many other goods for our daily living. Natural and man made materials are transformed to produce these things.
III. Fibres
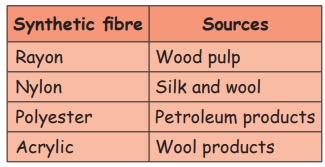
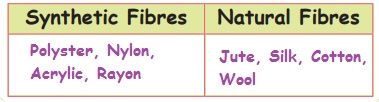
Fibre is a thin thread of natural or artificial substances. It is used to make cloths with the help of powerlooms or weaving machines. The fibres we get from plants and animals are called natural fibres. Cotton, jute, coir, flax, hemp are examples for plant fibres. Wool and silk are examples for animal fibres. Fibres made by humans by chemical synthesis are called synthetic fibres or artificial fibres. Rayon, nylon, acrylic and dacron are examples for artificial fibres. These fibres are obtained from petroleum by complex chemical processes.

1. Natural Fibres
• Cotton
A cotton plant is a bushy plant of 5 to 6 feet high. Cotton grows well in black soil and alluvial soil. The cotton plant bears a large number of small green pods called cotton balls. These balls contain seeds covered with white fibres. When the cotton balls mature, they burst exposing the white fibre of cotton. Cotton is usually hand picked from the plants.

Ginning
There are two processes to make cotton yarn from cotton fibre. The raw fibres are separated from the seeds by a process known as Ginning. The fibrous material left after separating cotton seeds is called lint. The lint is then tied and pressed into balls. The final proportions of short fibres and other impurities are removed by the process of combing.
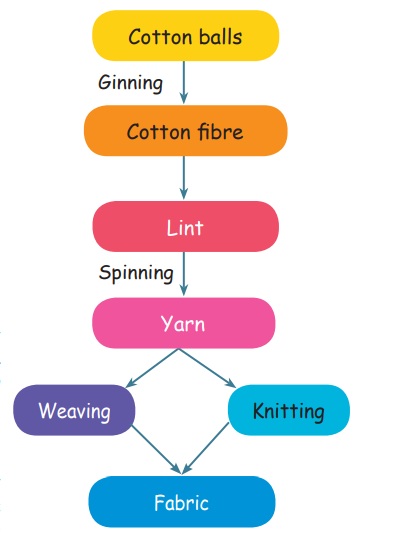
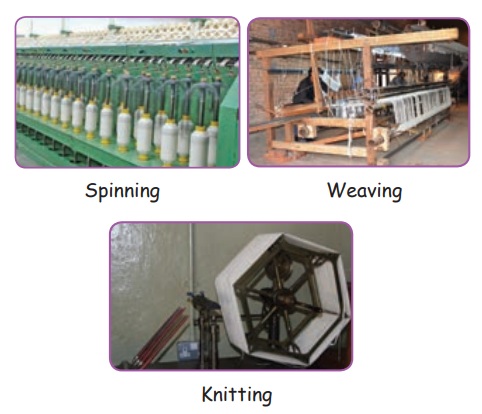
Spinning
The process of making yarn from lint (fibre) is called spinning. Spinning is done on a large scale with the help of spinning machines.
Yarn to fabrics
Weaving and knitting are the two most important processes used for making fabric from the yarn. The process of making two sets of yarns together to make fabric is called weaving. It is done by weavers on a machine called loom. The loom are either hand – operated (hand looms) or power – operated. During knitting a single yarn is used to make a piece of fabric. It is done by hand and also on machine.
Uses of cotton
• It is used to manufacture cotton textiles and garments.
• It is used as fillers in pillows and mattresses.
• It used for making surgical bandages.
• It is used for making dhotis, sarees, bedsheets, table cloth and so on.
• Jute
Jute fibre is obtained from the stem of the jute plant. Jute plant has long, soft and shiny fibres. It is also referred to as the golden fibre due to its colour and cost effectiveness. Jute fibres are separated from the process of retting jute by hand and then they are dried. These are converted into yarns in the same manner as in the case of cotton.

Uses of Jute
• It is used for making bags, carpets, curtains and ropes.
• It is used for making clothes for wrapping bales of raw cotton and to make socks for storing grains.
• It is used for making wall hangings for decoration.

• Coir
Coir fibre is obtained from the outer covering of coconut. It is used to make floor mats, door mats, brushes and mattresses.

2. Synthetic Fibres (or) Manmade Fibres
These fibres are made by human beings with the help of chemical process. Hence, they are called synthetic fibres or manmade fibres. These fibres are obtained from coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Activity 2
Classify the following natural fibres. Polyster, Jute, Silk, Nylon, Cotton, Wool, Acrylic, Rayon.
Uses of synthetic fibres
• Rayon is used to make rope, cloth, cap, tyre cords and carpets.
• Nylon is used to make fishing nets, ropes, parachutes, fabrics and bristles for brushes.
• Polyester is used to make fabric for suits and shirts, hoses, conveyer belts, films, PET bottles and wires.
• Acrylic is used to make sweaters, shawls and blankets.
Do you know?
The world‛s most valuable fibre is obtained from a small wild animal called Vicuna. It belongs to a camel family.

IV. Grains
Grain s a small, hard, dry seed. Each grain is protected by a husk and the husk encloses the seed. Two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legumes. Wheat, maize, rice, beans, peas, barley and millets are some of the whole grains.
• Wheat
This is the most important crop cultivated in the world. Whole wheat is important because it is rich in fibre, vitamins and minerals. Wheat products are: Breads, Cakes, Pasta, Wheat germ and Cracked wheat.

• Maize
In many tropical and sub tropical countries (Mexico and America), maize is the main food that people eat. It is also known as corn. Maize is also made into oil for cooking. Yellow or coloured corn may promote eye health. It is also rich source of many vitamins and minerals. Corn syrup is used as a sweetener instead of sugar in many products. Maize products are: Sweet corn, Breakfast cereal, Tortilla chips, Taco and Maize oil.

• Rice
Rice is a type of grass. It is produced worldwide after sugarcane and maize. Large parts of the world‛s human population especially people in Asia have this as their main food. Ninety percent of the world‛s rice production is in Asia. White rice contains few essential nutrients. Brown rice is a whole grain that contains the fibrous bran. Brown rice is usually considered much healthier than white rice. Rice idly, Idiappam and Rice aval (Flattened rice) are the food items made from rice.

• Millets
Millets are a group of small seeded grasses. They are widely grown around the world as cereal crops for fodder and human food. It helps in weight loss. It is rich in fibre. Some of the millet products are Sorghum, Fox tail millet, Finger millet, Pearl millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet and Little Millet.

V. Household Goods
These are the products that we use in our house. The goods that are found in a house permanently are called household goods. Household goods are: Furniture, Kitchenware, Cloths, Towels, Beddings, Boots and Electronic goods.
Household goods used in the olden days

Household goods used in the modern days

VI. Sinking and Floating
You could have seen that some objects float in water while others sink. Whether an object floats or sinks is determined by its density. When an object is immersed in a liquid, the liquid exerts an upward force on the object. It is known as upthrust. What happens if you put a coin and an empty water bottle in water? The weight of the coin is greater than the upthrust and so the coin sinks. But it is less on the empty water bottle and so it floats.

Activity 3
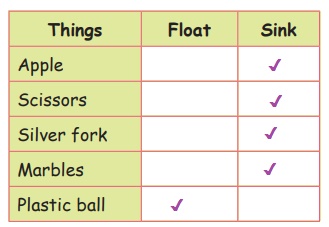
Take water in a bucket and drop the following items in the water.
Apple, Scissors, Silver fork, Marbles, Plastic ball.
Fill the table with your observation.
Do you know?
A fish can control the upthurst on its body. So it can float and go beneath the surface of the water.
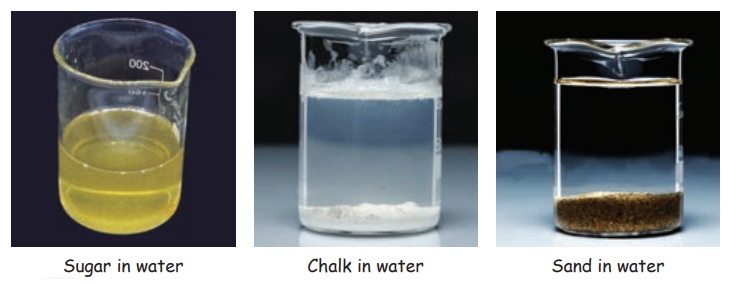
VII. Solubility of Solids in Water
Some substances completely dissolve in water. We say that these substances are soluble in water. Other substances do not dissolve in water even after we stir for long time. These substances are insoluble in water.
Activity 4
Collect some samples of solid substances such as salt, sugar, chalk powder, sand and saw dust.
Take five beakers filled with water and add a small amount of sugar to the first beaker, salt to the second and similarly, add small amounts of other substances in other beakers. Stir the content with a glass rod. Wait for few minutes. What happens to the substances added? Note your observation.

VIII. Mixing
Certain liquids are heavier (dense) than other liquids. When you attempt to mix liquids which have different densities they separate when you stop mixing them. The heavier liquid deposits at the bottom and the lighter liquid floats on the top.

Activity 5
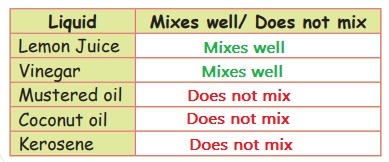
Collect samples of coconut oil, kerosene, mustard oil, lemon juice and vinegar. Take five test tubes, fill them up to half with water. Add a spoon full of one liquid to this and stir it well. Keep it in a test tube stand and wait for few minutes. Observe whether the liquid mixes with water. Repeat the experiment with other liquids and tabulate your observation.
Do you know?
• Substances with similar chemical properties will mix.
• Substances with different chemical properties will not mix.
Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. Which of the following are the states of matter?
a) Solid, Liquid, Water
b. Solid, Liquid, Gas
c) Solid, Liquid, Wood
d. Solid, Liquid, Sugar
Answer: b. Solid, Liquid, Gas
2. Which of the following is a solid?
a. Kerosene
b. Air
c. Water
d. Apple
Answer: d. Apple
3. Jute fibre is obtained from
a. leaf
b. stem
c. flower
d. root
Answer: b. stem
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Black soil is suitable for growing cotton.
2. The process of making cotton yarn from cotton fibre is spinning.
3. Ginning is done to separate raw fibres from the seeds.
4. Synthetic fibre is also called artificial fibre.
5. Woolen clothes are manufactured from animals ( plant / animals).
III. Match the following.
Yarn – Ginning
Lint – Spinning
Fabrics – Wood pulp
Rayon – Stem
Jute – Weaving
Answer:
Yarn – Spinning
Lint – Ginning
Fabrics- Weaving
Rayon- Wood pulp
IV. Say True or False.
1. Coir is the outer covering of coconut. (True)
2. Beans and peas are pulses. (True)
3. Table is a household good. (True)
4. Sweet corn is not a product of maize. (False)
Sweet corn is a product of maize.
5. Cotton balls contain jute fibre. (False)
Cotton balls contain cotton fibre.
V. Complete the given analogy.
1. Solid : Table :: Liquid: Water
2. Cotton seed : Ginning :: Lint: Spinning
3. Coir fibre: Coconut :: Cotton fibre : Cotton Plant
4. Black Pepper: Spice :: Sweat corn : maize product
VI. Answer in brief.
1. What is known as ginning?
The raw fibres are separated from the seeds by a process known as Ginning.
2. Give two examples for food products made from wheat.
Breads, Cakes and Pasta are made from wheat.
3. What are synthetic fibres?
These fibres are made by human beings with the help of chemical process. Hence, they are called synthetic fibres or manmade fibres.
4. What is known as upthrust?
When an object is immersed into a liquid, the liquid exerts an upward force on the object. It is known as upthrust.
5. Name the list of whole grains.
Grain is a small, hard, dry seed. Each grain is protected by a husk and the husk encloses the seed. Two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legumes. Wheat, maize, rice, beans, peas, barely and millets are some of the whole grains.
VII. Answer in detail.
1. Discuss briefly about three states of matter.

Solid: In solids molecules are very closely arranged. Solids are incompressible. They have definite shape, size and volume.
Liquids: In liquids molecules are loosely packed. Hence, liquids are negligibly compressible. They have definite volume, but no definite shape and size.
Gas: In gases, molecules are very loosely packed. Hence, gases are highly compressible.
2. Draw a flow chart to indicate the process of making fabrics from cotton ball.
The fibrous material left after separating cotton seeds is called lint. The lint is then tied and pressed into balls. The final proportions of short fibres and other impurities are removed by the process of combing.

Spinning : The process of making yarn from lint (fibre) is called spinning. Spinning is done on a large scale with the help of spinning machines.
Yarn to fabrics : Weaving and knitting are the two most important processes used for making fabric from the yarn. The process of making two sets of yarns together to make fabric is called weaving. It is done by weavers on a machine called loom. The looms are either hand – operated (hand looms) or power – operated. During knitting a single yarn is used to make a piece of fabric. It is done by hand and also on machine.
VIII. Give reason.
1. Why umbrellas are made up of synthetic clothes?
Synthetic clothes have greater hydrophobic quality (water repelling quality) but natural fibres absorb water more easily. Synthetic clothes do not absorb water and so umbrellas are made up of synthetic clothes.
2. What determines whether an object floats or sinks in a fluid?
When the weight of an object is greater than the upthrust of the fluid it sinks into it.
When the weight of an object is less than the upthrust of the fluid it floats on the fluid.
Activity 1
Look at your surrounding. Give some examples for solids, liquids and gases. Solids Liquids gases

Activity 2
Classify the following natural fibres. Polyster, Jute, Silk, Nylon, Cotton, Wool, Acrylic, Rayon.

Activity 3
Take water in a bucket and drop the following items in the water.
Apple, Scissors, Silver fork, Marbles, Plastic ball.
Fill the table with your observation.

Activity 4
Collect some samples of solid substances such as salt, sugar, chalk powder, sand and saw dust.
Take five beakers filled with water and add a small amount of sugar to the first beaker, salt to the second and similarly, add small amounts of other substances in other beakers. Stir the content with a glass rod. Wait for few minutes. What happens to the substances added? Note your observation.

Activity 5
Collect samples of coconut oil, kerosene, mustard oil, lemon juice and vinegar. Take five test tubes, fill them up to half with water. Add a spoon full of one liquid to this and stir it well. Keep it in a test tube stand and wait for few minutes. Observe whether the liquid mixes with water. Repeat the experiment with other liquids and tabulate your observation.















