Science : Chapter 12 : Atomic Structure
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
1. Choose the best answer.
1. The same proportion of carbon and oxygen in the carbon dioxide obtained from different sources proves the law of__________
a) reciprocal proportion
b) definite proportion
c) multiple proportion
d) conservation of mass
[Answer: (b) definite proportion]
2. Cathode rays are made up of
a) neutral particles
b) positively charged particles
c) negatively charged particles
d) None of the above
[Answer: (c) negatively charged particles]
3. In water, hydrogen and oxygen are combined in the ratio of _______by mass.
a) 1:8
b) 8:1
c) 2:3
d) 1:3
[Answer: (a) 1:8]
4. Which of the following statements made by Dalton has not undergone any change?
a) Atoms cannot be broken.
b) Atoms combine in small, whole numbers to form compounds.
c) Elements are made up of atoms.
d) All atoms of an elements are alike
[Answer: (d) All atoms of an elements are alike]
5. In all atoms of an element
a) the atomic and the mass number are same.
b) the mass number is same and the atomic number is different.
c) the atomic number is same and the mass number is different
d) both atomic and mass numbers may vary.
[Answer: (a) Valency]
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Atom is the smallest particle of an element.
2. An element is composed of same kind of atoms.
3. An atom is made up of proton, electron and neutron.
4. A negatively charged ion is called anion, while positively charged ion is called cation.
5. Electron is a negatively charged particle (Electron/Proton).
6. Proton is deflected towards the negatively charged plate (positively, negatively).
III. Match the following.
Law of conservation of mass – Sir William Crookes
Law of constant proportion James – Chadwick
Cathode rays – Joseph Proust
Anode rays – Lavoisier
Neutrons – Goldstein
Answer:
1. Law of Conservation of Mass – Lavoisier
2. Law of Constant Proportion – Joseph Proust
3. Cathode rays – Sir William Crookes
4. Anode rays – Goldstein
5. Neutrons – James Chadwick
IV. Answer briefly.
1. State the law of conservation of mass.
Answer: The law states that during any chemical change, the total mass of the products is equal to the total mass of the reactants.
2. State the law of constant proportions.
Answer: Law of constant proportions states that in a pure chemical compound the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
3. Write the properties of anode rays.
Answer: Properties of Anode rays:
(i) Anode rays travel in straight lines.
(ii) Anode rays are made up of material particles.
(iii) Anode rays are deflected by electric and magnetic fields. Since, they are deflected towards the negatively charged plate, they consist of positively charged particles.
4. Define valency of an element with respect to hydrogen.
Answer: Valency of an element is defined as the number of hydrogen atoms which combine with one atom of it.
5. Define the term ions or radicals.
Answer: An atom or a group of atoms when they either lose or gain electrons, get converted into ions or radicals.
6. What is a chemical equation?
Answer: A chemical equation is a short hand representation of a chemical reaction with the help of chemical symbols and formulae.
7. Write the names of the following compounds.
a) CO
b) N2O
c) NO2
d) PCl5
Answer:
a. Carbon monoxide.
b. Nitrous oxide
c. Nitrogen dioxide
d. Phosphorous pentachloride
V. Answer the following.
1. Find the valency of the element which is underlined in the following formula.
a) Na Cl
b) C O2
c) Al (PO4)
d) Ba (NO3)2
e) CaCl2
Answer:
a) NaCI = 1
b) CO2 = 4
c) Al(PO4)= 3
d) Ba(NO3)2 = 2
e) CaCl2 = 2
2. Write the chemical formula for the following compounds
a) Aluminium sulphate
b) Silver nitrate
c) Magnesium oxide
d) Barium chloride
Answer:
a. Aluminium sulphate = A12(SO4)3
b. Silver nitrate = AgNO3
c. Magnesium oxide = MgO
d. Barium chloride = BaCl2
3. Write the skeleton equation for the following word equation and then balance them.
a. Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide
b. Phosphorus + Chlorine → Phosphorus pentachloride.
c. Sulphur + Oxygen → Sulphur dioxide
d. Magnesium + hydrogen → Magnesium + Hydrogen chloride chloride
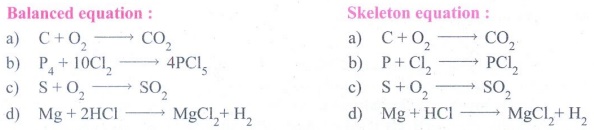
Balanced equation :
a) C + O2 → CO2
b) P4 + 10Cl2 → 4PCl5
c) S + O2 → SO2
d) Mg + 2HCI → MgCl2 + H2
Skeleton equation :
a) C + O2 → CO2
b) P4 + Cl2 → PCl2
c) S + O2 → SO2
d) Mg + HCI → MgCl2 + H2
4. Balance the following chemical equation.
a. Na + O2 → Na2O
b. Ca + N2 → Ca3N2
c. N2 + H2 →NH3
d. CaCO3 +HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 +H2O
e. Pb(NO3)2 → PbO + NO2 + O2
a) 4Na + O2 → 2Na2O
b) 3Ca + N2 → Ca3N2
c) N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
d) CaCO3 + 2HCI → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
e) 2Pb (NO3)2 → 2PbO + 4N02 + O2
VI. Higher Order Thinking Questions.
1. Why does a light paddle wheel placed in the path of cathode rays begin to rotate, when cathode rays fall on it?
Answer: It is because the small particles of the cathode rays (electrons) have mass and energy. This energy is used in rotating the paddle wheels.
2. How can we prove that the electrons carry negative charge?
Answer: J.J. Thomson found that cathode rays were attracted by the positively charged plate and repelled by the negatively charged plate. This led him to the conclusion that the cathode rays (electrons) were made of negatively charged particles.
3. Ruthresh, Hari, Kanishka and Thahera collected different samples of water from a well, a pond, a river and underground water. All these samples were sent to a testing laboratory. The test result showed the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen as 1:8.
a) What conclusion would you draw fromthe above experiment?
b) Which law of chemical combination does it obey?
Answer: a) Water obtained from different sources like a well, a pond, a river and underground water will always consist of the same two elements hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio 1 : 8 by mass.
b) It obeys the law of constant proportion.
Student Activities
Activity 1
Collect more information about the properties of fundamental particles and prepare a chart.
Activity 2
Classify the following ions into monovalent, divalent and trivalent.
Ni2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, Ba2+, Cs+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ Pb2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Sr2+, Cr3+, Li+, Ca2+, Al3+
Answer:
Monovalent ions : Li+, Cs+
Divalent ions : Ni2+, Cu2+, Ba2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ca2+, Sr2 Trivalent ions : Fe3+, Cr3+, Al3+
Activity 3
Write the chemical formula of the compounds
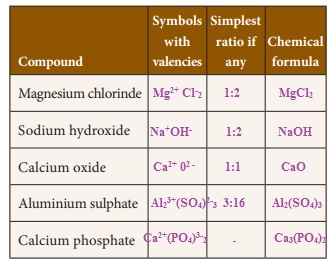
Activity 4
Write the names of the chemical compounds.
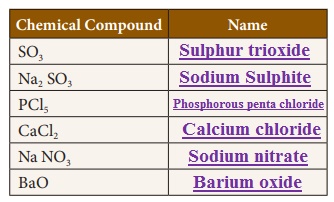
Activity 5
Take some ice cubes in an air tight container and note the weight of the container with ice cubes. Wait for a while for the ice cubes to become water. It is a physical change ie., ice cubes melt and they are converted into liquid. Now weigh the container and compare the weight before and after the melting of ice cubes. It remains the same. Hence it is proved that during a physical change, the total mass of matter remains the same.
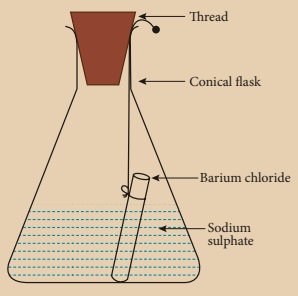
Activity 6
Prepare 5% of barium chloride (5g of BaCl2 in 100 ml of water) and sodium sulphate solutions separately. Take some solution of sodium sulphate in a conical flask and some solution of barium chloride in a test tube. Hang the test tube in the conical flask. Weigh the flask with its contents. Now mix the two solutions by tilting and swirling the flask. Weigh the flask after the chemical reaction is occurred. Record your observation. It can be seen that the weight of the flask and the contents remainsthe same before and after the chemical change. Hence, it is proved that during a chemical change, the total mass of matter remains the same.
John Dalton, son of a poor weaver, began his career as a village school teacher at the age of 12. He became the principal of the school seven years later. In 1793, he moved to Manchester to teach Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics in a college. He proposed his atomic theory in 1803. He carefully recorded each day, the temperature, pressure and amount of rainfall from his youth till the end. He was a meticulous meteorologist.

Electricity, when passes through air, removes the electrons from the gaseous atoms and produces cations. This is called electrical discharge.
The fact that air is a poor conductor of electricity is ablessing in disguise for us. Imagine what would happen if air had been a good conductor of electricity. All of us would have got electrocuted, when a minor spark was produced by accident.
In television tube cathode rays are deflected by magnetic fields. A beam of cathode rays is directed toward a coated screen on the front of thetube, where by varying the magnetic field generated by electromagnetic coils, the beam traces a luminescent image.
When invisible radiation falls on materials like zinc sulphide, they emit a visible light (or glow). These materials are called fluorescent materials.
When hydrogen gas wastaken in a discharge tube, the positively charged particles obtained from the hydrogen gas were called protons. Each of these protons are produced when one electron is removed from one hydrogen atom. Thus, a proton can be defined as an hydrogen ion (H+).
H → H+ + e–














