Science : Term 3 Unit 1 : Light
EVALUATION
I. Choose the correct option
1. Light travels only in a . It is because of this property that are formed
a. curved line, shadows
b. straight line, shadows
c. straight line, reflection
d. curved line and then straight line, shadows
[Answer: (b) straight line, shadows]
2. Light that hits a mirror gets
a. Transmitted
b. Reflected
c. Absorbed
d. Refracted
[Answer: (b) Reflected]
3. Surface reflects the light well.
a. water
b. compact disc
c. mirror
d. stone
[Answer: (c) Mirror]
4. Light is a form of
a. matter
b. energy
c. medium
d. particle
[Answer: (b) energy]
5. You can see your image in polished floors, but not in wooden table because
a. regular reflection takes place in wooden table and irregular reflection in polished floor
b. regular reflection takes place in polished floor and irregular reflection in wooden table
c. regular reflection takes place in both polished floor and wooden table
d. irregular reflection takes place in both polished floor and wooden table
[Answer: (b) regular reflection takes place in polished floor and irregular reflection in wooden table]
6. Choose the translucent substance from the following
a. glass
b. wood
c. water
d. Clouds
[Answer: (d) Clouds]
7. Reflection occurs , when the light
a. about to reach a surface
b. approaches a surface
c. passes through a surface
d. None of these
[Answer: (b) approaches a surface]
8. Which of the following is the best reflector of light?
a. plastic plate
b. plane mirror
c. wall
d. paper
[Answer: (b) plane mirror]
9. Sivarajan placed a meter stick in the playground at 7.00 am in the morning. How will the shadow of the stick at noon look in comparison to the one in the morning
a. There will be no shadow
b. The shadow will be longer and on the opposite side as the sun
c. The shadow will be shorter and on the same side as the sun
d. The shadow will be shorter
[Answer: (d) The shadow will be shorter]
10. The image formed by a pinhole camera is in-verted because,
a. light travels in straight lines
b. light rays become laterally inverted as they pass through a pinhole camera
c. light rays pass through the pinhole
d. light rays get reflected
[Answer: (a) light travels in straight lines]
11. Which of the following facts explain how shadows are formed?
a. Light travels in straight lines
b. Opaque bodies do not allow light to pass through them
c. Reflection occurs at a smooth surfaces like mirrors
d. Lateral inversion happens
a. both A and B
b. both A and D
c. both B and C
d. only A
[Answer: (a) both A and B]
II. Fill in the blanks
1. A plane mirror produces a virtual and erect image
2. A regular reflection helps us to see the objects
3. The light ray gets reflected when it falls on any polished surface.
4. Sunlight is a blend of seven colors
5. The splitting of white light in to seven colors is called dispersion.
6. The moon reflects sun light
7. The sunlight can be split into its constituent colors using prism.
8. Reflection of light from rough surface is called irregular reflection
III. Say TRUE or FALSE
1. The image of right hand in a plane mirror looks like a left hand Answer: True
2. Rainbow is formed by dispersion of which light by water drops Answer: True
3. The image formed by the plane mirror is laterally inverted, hence the image seen through the periscope is also laterally in-verted Answer: False.
Correct statement: The image formed by the plane mirror is laterally inverted, hence the image seen through the periscope is erect. This is because in periscope, image is reflected by two mirrors.
4. We see planets because they reflect light from the sun Answer: True
5. We see a book because it reflects the light that falls on its surface Answer: True
6. The image formed in a pinhole camera is always inverted Answer: True
7. The image formed in a pinhole camera is always the same size as the object Answer: False.
8. The image formed in a plane mirror is upside down Answer: False.
Correct statement: The image formed in a plane mirror is erect.
9. A plane mirror is opaque Answer: True
10. A shadow is formed on the same side of the object as the source of light. Answer: False.
Correct statement : A shadow is formed on the opposite side of the object as the source of light.
11. we are able to see things around us with the help of regular reflection Answer: True
12. After passing through a prism, white light splits into a band of seven colours Answer: True
IV. Match the following
Rectilinear propagation – Primary source of light
Plane Mirror – Non-luminous object
Fire fly – Periscope
The Moon – Pinhole camera
Wide light source – Spectrum of light
Regular reflection – luminous object
The sun – Penumbra
Band of seven colors – Glossy surface
Answer:
1. Rectilinear propagation – Pinhole camera
2. Plane Mirror – Periscope
3. Fire fly – Luminous object
4. The Moon – Non-luminous object
5. Wide light source – Penumbra
6. Regular reflection – Glossy surface
7. The sun – Primary source of light
8. Band of seven colors – Spectrum of light
V. Answer the following questions in short
1. With the help of a diagram, state the laws of reflection
Answer: Laws of reflection:
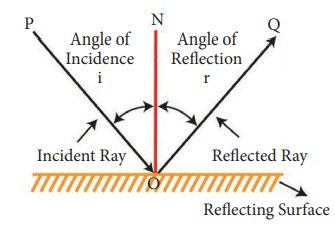
(i) The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection ∠i = ∠x
(ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie on the same plane.
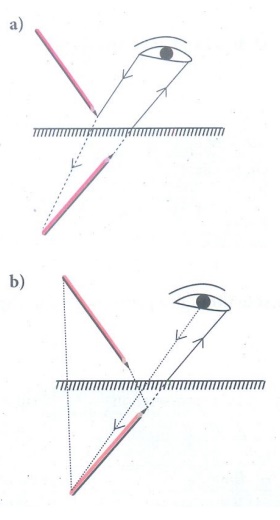
2. Figure shows a pencil placed above a mirror
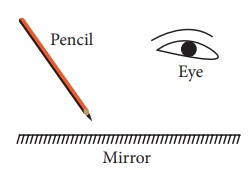
a. Draw its image formed by the mirror
b. Show how light rays from the object are reflected at the mirror to form the image for the eye.
Answer:
3. A person is looking at the image of a tree in a mirror placed 3.5 m in front of him. Given that the tree is at 0.5 m behind his eyes. Find the distance between the image of the tree and his eyes. What are needed to see an object?
Answer:
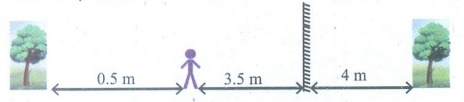
Distance between the person and the mirror = 3.5 m
Distance between the person and tree (object) = 0.5 m.
The image formed in the mirror = 4 m
The distance between the image of the tree and his eyes = 4 + 3.5 = 7.5 m
Things needed to see an object :
❖ Source of light
❖ Object
❖ Eyes
4. What are luminous objects?
Answer: All objects which emit light energy by themselves are called luminous objects. Ex.: Sun, electric bulb.
5. Is the moon a luminous object?
Answer: No, the moon is non-luminous. The reason is that moon does not produce its own light. Instead, it reflects the light of the sun falling on it.
6. What are the three types of materials based on the absorption of light?
Answer:
(i) Transparent Material
(ii) Translucent Material
(iii) Opaque Material
7. What are the parts of shadow?
Answer: (i) Umbra (ii) Penumbra
8. What are the properties of shadow?
Answer: Properties of shadow :
(i) All objects do not form shadows. Only opaque objects form shadows.
(ii) Shadows will be formed in the opposite side of light source.
(iii) It cannot be determined the characteristics of an object by its shadow.
(iv) The shadow will be always darker, whatever may be the color of light rays.
(v) Light source, opaque object are shadow all are in a straight line.
(vi) The size of shadow depends upon the distance between light source and object and the distance between object and the screen.
9. What is plane mirror?
Answer: A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat reflective surface. A plane mirror makes an image of objects in front of it.
10. What is prism?
Answer: A prism is an object made up of a transparent material, like glass or plastic that has at least two flat surfaces that form an acute angle (less than 90°).
11. What do you mean by visible light?
Answer: Visible light is a spectrum of a number of waves with different wavelength range from 400nm to 700nm (1 nm.= 10-9 meter) each wave has a definite wavelength represents a particular colour.
12. Write the items given here in the correct column (Stars, brick walls, plants, mirror, planets, electric light bulb, candle)
Answer:
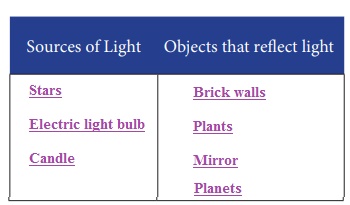
Sources of Light : Stars, Electric light bulb, Candle
Objects that reflect light : Brick walls, Plants, Mirror , Planets
13. A boy of height 1m 45 cm is standing in front of a long mirror at a distance of 2 m. From this information, fill up the following sentences:
a. The distance between the boy and his image is 4m.
b The height of the image is same.
c. When the boy moves 1m forward, the distance between her and her image is 2m.
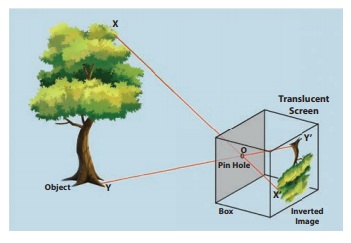
14. Draw a diagram of a pin hole camera showing the rays of light passing between the Object and its image
Answer:
15. Why is the writing on the front of an ambulance back to front as shown in the picture?

Answer:
(i) This is due to lateral inversion.
(ii) The phenomenon due to which the left side of an object appears to be right side of the object in its image in a reflecting medium (mirror).
(iii) So that drivers see the word the right way around in their rear-view mirror.
16. Explain with examples, why some capital letters look the same in a mirror but others are reversed.
Answer: Any letter that has a bilateral symmetry will have its mirror image the same as that of the object.
Example:
A | A
H | H
17. Two plane mirrors M1 and M2 are placed perpendicular with each other, as shown in figure. The ray AB makes an angle 39 ° with the plane mirror M1, then
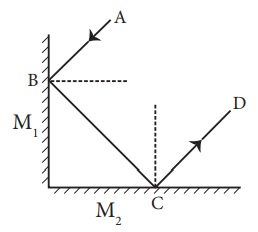
1. The reflected rays are , ____________,____________
2. The incident rays are , ____________,____________
3. What is the angle of incident corresponding to the ray BC?
4. What is the angle of reflection corresponding to the ray CD
Answer:
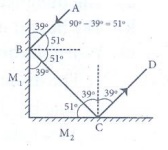
1. BC, CD
2. AB , BC
3. ∟i =39°
4. ∟r =39°
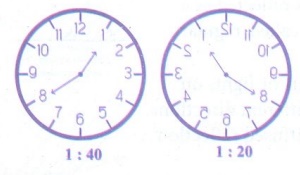
18. Rajan was playing with the mirror images of a clock. He looked at the clock in his room. It was showing 1:40. Draw the position of the hands on the real clock and on its mirror reflection. Write below the picture what time each picture is showing.
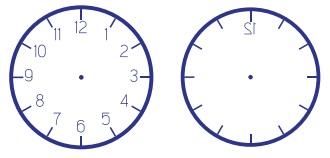
Answer:
19. What is reflection of light?
Answer: The bouncing back of light from a reflecting surface of an object is called as reflection of light.
20. If a ray of light is falling on a plane mirror at an angle of 500 is formed, what will be the angle of reflection?
Answer:
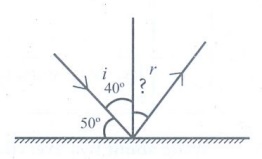
Angle of incidence
∟i = 90° – 50°
∟i = 40°
According to laws of reflection,
∟i = ∟r
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
∟i = 40°
∴ ∟r = 40°
Angle of reflection ∟r = 40°
21. What do you mean by lateral inversion?
Answer: The phenomenon due to which left hand side of object appears as right hand side and vice versa is called lateral inversion.
22. How do you obtain a spectrum of light?
Answer: When white light is made to fall on the surface of a prism, it disperses and we obtain a spectrum of light.
23. Why do we see white color in Newton’s disc, when we rotate it very fast?
Answer: When the disc turned quickly, the retina receives the sensation of the spectrum simultaneously and disc appears white.
24. What is a shadow? What things are necessary for the formation of a shadow?
Answer:
(i) Shadows are formed because light travels in straight lines.
(ii) Shadow is always against, opposite side of light source.
(iii) Shadow is formed by opaque objects that stop high from propagating.
(iv) Things necessary for the formation of shadow: source of light, opaque object.
VI. Answer the following questions in detail
1. What are regular and irregular reflection? Explain with the help of diagrams
Answer:
(i) Regular reflection : When a parallel beam of light on striking some smooth and polished surface is reflected as a parallel beam of light, such a reflection is called regular reflection.
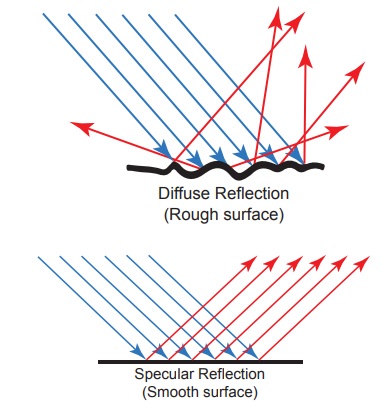
(ii) Irregular reflection : When a parallel beam of light, on striking some rough surface, is reflected in different directions, then such a reflection is called irregular or diffused reflection.
2. What are the difference between luminous and non-luminous objects? Give two examples of each.
Answer:

Luminous Objects
1.All objects which emit light energy by themselves are called luminous objects.
2. Ex : Sun, stars torch light burning candle etc.
Non -Luminous Objects
1. All objects which do not emit light energy of their own, but reflect the light energy falling on them and hence, become visible are called non- luminous object.
2. Ex : Metals, trees, houses, stones, moon etc.
3. Write about two everyday situations that tell you that light travels in a straight line.
Answer:
(i) Formation of shadow: Shadows are formed when some light rays continue its travel in straight lines while other rays are stopped by an object.
(ii) When there is a small hole in a room, light travels only in a straight line.
4. Differentiate between a reflection and a shadow
Answer:

Reflection
1. When light falls on a surface, the direction of ray is changed. This change in direction is known as reflection of light.
2. Eg.: You see your reflection in a pool of water or mirror.
Shadow
1.Shadow is an image formed by obstruction of light.
2. Eg. : If you place your hand in front of a candle, you will see the image of the hand on the wall. This image will show only the outline of the object placed in front of the light source.
5. What are the characteristics of an image formed in a plane mirror?
Answer:
(i) Image formed in a plane mirror is upright.
(ii) Image formed in a plane mirror is virtual
(iii) The image is of the same size as the object
(iv) The distance of the image from the plane mirror is equal to the distance of the object from the mirror.
(v) Image is laterally inverted.
6. Describe the pictures.
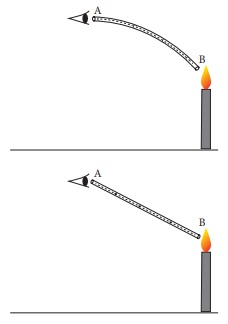
Answer:
(i) When the tube is bent, we cannot see the source of light.
(ii) When the tube is held straight we can see the flame. The two pictures verify that light travels in straight lines. This is known as rectilinear propagation of light.
7. Define the following terms
a. Incident ray
b. Reflected ray
c. Normal
d. Angle of incidence
Answer:
(a) Incident ray: The ray of light that falls on the surface of the reflection materials.
(b) Reflected ray: The ray of light that comes from the point when the incident ray falls on the reflection material.
(c) Normal: The perpendicular line drawn from the point of incidence to the plane of reflecting surface is called normal.
(d) Angle of incidence: The angle formed between the incident ray PO and the normal ‘ON’ is angle of incidence.
8. Compare the images formed by plane mirror with that by pinhole camera
Answer:
Difference between the images formed in Pinhole camera and Plane mirror :
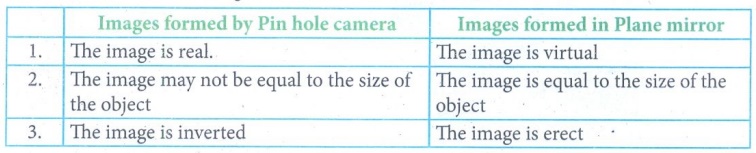
Images formed by Pin hole camera
1. The image is real.
2. The image may not be equal to the size of the object
3. The image is inverted
Images formed in Plane mirror
1.The image is virtual
2. The image is equal to the size of the object
3. The image is erect
Numerical problems
Laws of reflection:
Example 1
In the figure, the incident ray makes 27° with the normal, then find the angle of reflection.
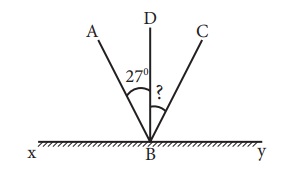
Solution:
Angle of incidence = 27°
According to the laws of refelection, the angle of refelection = Angle of incidence = 27°
Example 2:
A light ray strikes a reflective plane surface at an angle of 43° with the plane surface.
i. Find the angle of incidence.
ii. Find the angle of reflection.
iii. Find the angle between the incident and the reflected ray
iv. Find the angle between the reflected ray and the plane surface.
Solution:
We use the diagram shown below to answer the questions.
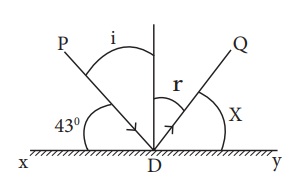
a. Angle of incidence: i = 90 -43 = 47°
b. angle of reflection r = i = 47°
c. i + r = 47 + 47 = 94°
d. x = 90 – r = 90 – 47 = 43°
Q. A person is looking at the image of a tree in a mirror placed 3.5 m in front of him. Given that the tree is at 0.5 m behind his eyes. Find the distance between the image of the tree and his eyes. What are needed to see an object?
Answer:

Distance between the person and the mirror = 3.5 m
Distance between the person and tree (object) = 0.5 m.
The image formed in the mirror = 4 m
The distance between the image of the tree and his eyes = 4 + 3.5 = 7.5 m
Things needed to see an object :
❖ Source of light
❖ Object
❖ Eyes
Q. A boy of height 1m 45 cm is standing in front of a long mirror at a distance of 2 m. From this information, fill up the following sentences:
a. The distance between the boy and his image is 4m.
b The height of the image is same.
c. When the boy moves 1m forward, the distance between her and her image is 2m.
Q. Draw a diagram of a pin hole camera showing the rays of light passing between the Object and its image
Answer:

Q. Two plane mirrors M1 and M2 are placed perpendicular with each other, as shown in figure. The ray AB makes an angle 39 ° with the plane mirror M1, then

1. The reflected rays are , ____________,____________
2. The incident rays are , ____________,____________
3. What is the angle of incident corresponding to the ray BC?
4. What is the angle of reflection corresponding to the ray CD
Answer:

1. BC, CD
2. AB , BC
3. ∟i =39°
4. ∟r =39°
Q. Rajan was playing with the mirror images of a clock. He looked at the clock in his room. It was showing 1:40. Draw the position of the hands on the real clock and on its mirror reflection. Write below the picture what time each picture is showing.

Answer:

Q. If a ray of light is falling on a plane mirror at an angle of 500 is formed, what will be the angle of reflection?
Answer:

Angle of incidence
∟i = 90° – 50°
∟i = 40°
According to laws of reflection,
∟i = ∟r
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
∟i = 40°
∴ ∟r = 40°
Angle of reflection ∟r = 40°
Student Activities
ACTIVITY 1
Requirement: Three empty match boxes, pin, candle and wooden blocks.
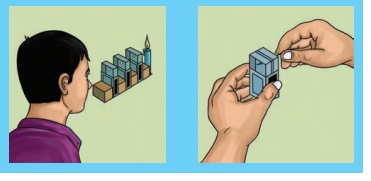
Procedure: Arrange empty match boxes and wooden blocks as shown in the figure. First, you make a hole in the inner tray of each match box such that all three holes are in the same spot. Arrange the match boxes as shown in figure. Now, adjust the three inner trays in such a way that the three holes are in a straight line. Place a lighted candle at one end of this arrangement and try to see the flame of candle from a hole at the other end. Is the flame visible?
Now, arrange the trays such a way that they are not at the same height. Try to see the flame. Is it visible? What does this activity tell you about the path of light?
Light travels in straight line, it cannot bend the path itself. This is called as the rectilinear propagation of light. This is one of the most important property of light.
ACTIVITY 2
Make your pin-hole camera
Requirement : Two rectangular pieces of thick paper, carbon paper, a semi-transparent paper, adhesive
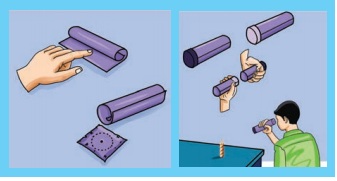
Procedure : Make two tubes using thick paper as shown in figure. One tube should be slightly smaller in diameter so that it can slide into the other tube without leaving much gap between the tubes. Fix a carbon paper to one side of the tube of greater diameter. Make a hole with a pin at the center of the carbon. Close one end of the second tube with the butter paper. Slide the smaller tube into the bigger one such a way that the butter paper is inside. Keep a lighted candle on a table and look through the hole with black side towards the candle. If you go closer to the candle, you will see a smaller, but brighter image. You can also change the image size by adjusting the tubes.
Use the pin-hole camera to see things in sun light outside the window and see how good an image you get. What are your observations about the image? Is it straight, inverted, bright and sharp?
ACTIVITY 3
Make your own periscope : You can use an empty agarbathi box and two plane mirrors to make a periscope.
As shown in the figure below, two plane mirrors are kept 45 degrees to horizontal.
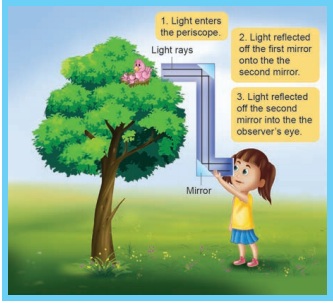
As shown the figure above, the light rays from the distant object enter through the tube at 1, and hit the mirror at 2. As the angle of incident must be equal to angle of reflection, the reflected rays flow through the tube downwards. As the light rays hit the mirror at 3 once again they are reflected. This reflected rays then travel out of the box to our eye. As you can see, periscope uses the laws of reflection.
ACTIVITY 4
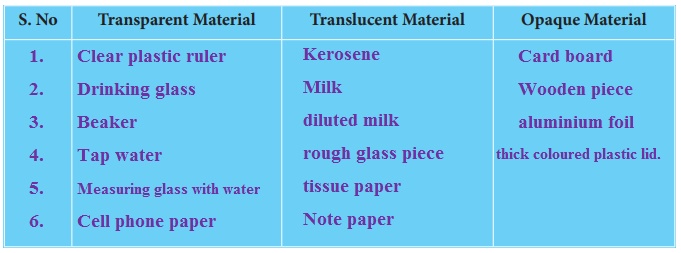
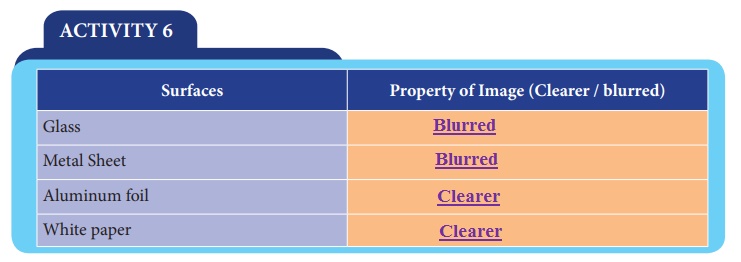
Let’s categorize transparent material, translucent material and opaque material among the given materials
(Clear plastic ruler, cellophane paper , some water in a glass jar, tissue paper, drinking glass, beaker, tap water, kerosene, coconut oil, note paper, card board, milk, diluted milk, aluminum foil, thick colored plastic lid, rough glass piece, measuring glass with water, wooden piece)
Place all the materials given above in the dark room. Focus a torch light on one side of each material. Inspect the light coming out at the other side of each material and then classify the materials in the table.
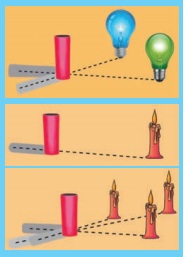
ACTIVITY 5
Requirement : A white screen, a cylindrical opaque object and three bulbs in different sizes.
Use the three different size lamps and examine the umbra and penumbra formed. Keep the distance between the lamp and the cylinder, cylinder and the screen same. As the size of the lamps grow smaller, the umbra region begins to enlarge. If the size of the lamp is a point, then there will be no penumbra. There would be only umbra shadow. Can you tell what the reason is for that?
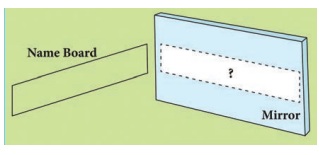
ACTIVITY 7
There are eight letters in the word EINSTEIN
1. Write the word in front of a plane mirror shown in diagram
2. Write down how these letters appear in the mirror
3. How many of these letters appear to be different, when the word is reflected?
4. Write down the letters that appear to be the same.
Answer:
(i) 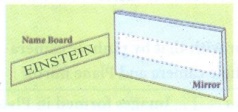
(ii) 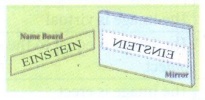
(iii) 3 letters (E, N, S)
(iv) I, T
ACTIVITY 8
We have seen that white light is made of different colors and we can split white light. Is it possible to do the reverse? That is, can you get white color by mixing colors? Try this activity.
You need oil pastel and white paper. Take different oil pastel colors. Choose colors which are exactly seen on the rainbow. Apply colors over each other on a white paper. Did you get white color?

ACTIVITY 9
Let’s make a rainbow
You must surely have seen a rainbow in the sky. Why don’t you try making one at your class room?
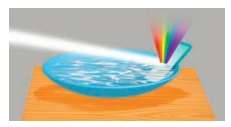
Place a flat but deep pan. Place this pan where there is direct sunlight. Place a plain mirror in the pan as shown in the diagram, so that you see sunlight reflected on you ceiling or on a white wall. Next slowly pour water in to the pan. At particular level of water, you will get a beautiful rainbow colors on the wall. If the colors are not clear adjust the position of the mirror to bring it into focus. This arrangement of colors in sunlight is called spectrum.
ACTIVITY 10
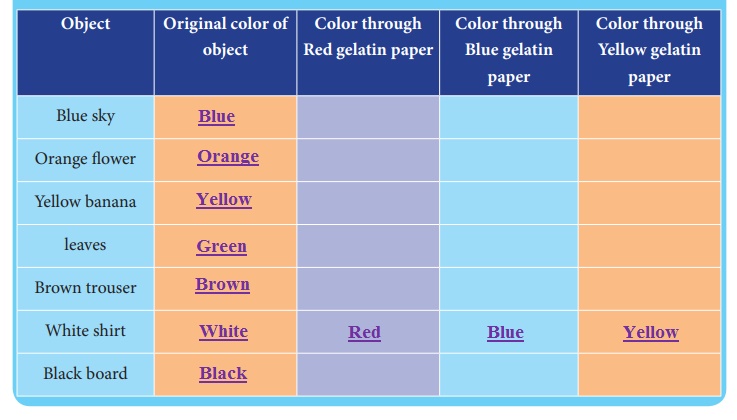
You need Gelatin papers of Red, Blue and Yellow. Fold each gelatin paper three times and look different color objects listed below through each folded paper. Observe what color each object has. Write your observations in the table.
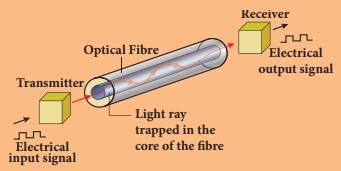
Optical fibre is a device that works on the principle of total internal reflection by which light Transmitter output signal signals (huge data) can be transmitted from one place to another place with a negligible loss of Light ray trapped in the energy in a very short time. It consists of a cable Electrical core of the bre having one or more thin flexible fibers with input signal a glass core through which light signals can be sent. Optical fiber can be twisted and bent easily. When a light a ray of light is incident at one end of the core of optical fiber, it suffers total internal reflection at the many places inside the fiber and emerges at the other end with negligible loss of energy. The data or information in the form of pulses of light, can be sent through bundles of optical fibers. Optical fibers have become very important in high-speed communications, such as cable TV and high-speed broadband services. Fiber optic cables are able to carry more signals than traditional copper cable telephone lines.

Is the moon a luminous object?
The moon provides light as well, but it cannot produce light by its own. The light emitted by the Moon is the light of the Sun reflected towards the Earth. When we see the Moon, we see only the Moon’s lighted part. Thus, half of the moon is always facing the Sun and receiving light from it. Hence, we receive light from the moon.

We often use a kind of gas- discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. The electric current in the gas excites mercury vapour, which produces short-wave ultraviolet light that then causes a phosphor coating on the inside of the lamp to glow in visible light.

Light is the only source of energy for plants. So, they entirely depend on light. People and animals derive energy from carbohydrates, protein and fat through their food. Plants produce food using the energy from Sun light, carbon-di-oxide and water by the process called as Photosynthesis. Sun light acts a vital role in the process of photosynthesis.

Al-hasan -Haytham was ascientific thinker who made important contribution to the understanding of vision, optics and light. He observed that light coming through a tiny hole travelled in straight lines and projected an image onto the opposite wall. Based on such experimentation, he concluded that vision is accomplished by rays coming from external luminous sources and entering the eye, rather than through rays emitted from the eye as was then commonly believed. He is the first one to experiment with light and found important properties like the rectilinear propagation of light.

Before the advancement of camera, Pinhole camera was used to photograph movement of the sun over a long period of time. This type of photography is known as solography and also be used for observing and recording solar eclipses. And it was also used to take photograph of stationary objects.

Why is the word “AMBULANCE” written backwards in ambulance vehicle? This is due to lateral inversion .The phenomenon due to which the left side of an object appears to be right side of the object in its image in a reflecting medium (mirror). so that drivers see the word the right way around in their rear-view mirror
Why danger lights in vehicles are red in colour?

1. Red color is scattered the least by air molecules.
2. Red color has the highest wavelength of all the other colors. So red color is able to travel the longest distance through air, fog.














